Appearance
useRoutes
matchRoutes
let matches = matchRoutes(routes, { pathname: remainingPathname });
作用
根据配置的路由信息 和 当前的路由地址 pathname,获取路由配置信息中匹配的路由数据
源码
ts
export function matchRoutes<
RouteObjectType extends AgnosticRouteObject = AgnosticRouteObject
>(
// 当前的路由配置数据
routes: RouteObjectType[],
// 当前 location 对象
locationArg: Partial<Location> | string,
basename = "/"
): AgnosticRouteMatch<string, RouteObjectType>[] | null {
// 获取真正的 pathname 值
// location 为 string 类型的 => 转换成 { pathname : , search , hash }
// location 为 对象类型的 直接返回
let location =
typeof locationArg === "string" ? parsePath(locationArg) : locationArg;
let pathname = stripBasename(location.pathname || "/", basename);
if (pathname == null) {
return null;
}
// 扁平化路由配置信息
let branches = flattenRoutes(routes);
// 根据权重 和 childrenIndex 对扁平化数据进行排序
rankRouteBranches(branches);
let matches = null;
for (let i = 0; matches == null && i < branches.length; ++i) {
// 遍历扁平化的 routes,查看每个 branch 的路径匹配规则是否能匹配到 pathname
matches = matchRouteBranch<string, RouteObjectType>(
branches[i],
// 解码 pathname
safelyDecodeURI(pathname)
);
}
return matches;
}分析
对于路由匹配的流程其主要分为几个步骤
1. 处理 location
在这一步骤中主要根据 location 对象 和 basename 从而获取到真正的 pathname 的过程
转换
locationArg, 对于matchRoutes(routes , "/app/home/homepage?name=1#b")这种不传入 location 对象 而传入字符串类型的页面地址的,那么就需要通过parsePath(locationArg)将其转换成 location 对象处理 basename ; 对于
matchRoutes(routes , "/app/home/homepage?name=1#b" , "/app")这种存在 basename 的,那么就需要将 pathname 中 basename 部分移除,从而获取真正的路由地址
ts
// 获取真正的 pathname 值
// location 为 string 类型的 => 转换成 { pathname : , search , hash }
// location 为 对象类型的 直接返回
let location =
typeof locationArg === "string" ? parsePath(locationArg) : locationArg;
let pathname = stripBasename(location.pathname || "/", basename);2. 扁平化路由配置信息
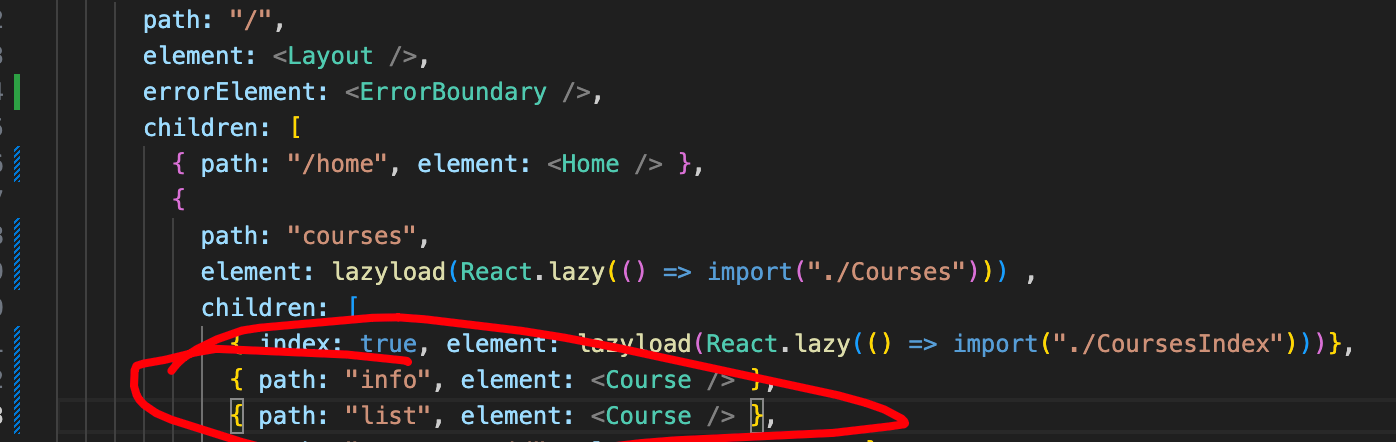
这个步骤中主要是将树形的路由配置信息转换一维数组的过程,如
ts
let routes: RouteObject[] = [
{
path: "/",
element: <Layout />,
errorElement: <ErrorBoundary />,
children: [
{ path: "/home", element: <Home /> },
{
path: "courses",
element: lazyload(React.lazy(() => import("./Courses"))),
children: [
{
index: true,
element: lazyload(React.lazy(() => import("./CoursesIndex"))),
},
{ path: "/courses/:id", element: <Course /> },
],
},
{ index: true, element: <MyNavigate to={"/courses"} replace={true} /> },
],
},
];其结果如下
ts
[
{ path: "/home", score: 13, routesMeta: Array(2) },
{ path: "/courses/", score: 17, routesMeta: Array(3) },
{ path: "/courses/:id", score: 17, routesMeta: Array(3) },
{ path: "/courses", score: 13, routesMeta: Array(2) },
{ path: "/", score: 6, routesMeta: Array(2) },
{ path: "/", score: 4, routesMeta: Array(1) },
];
其中比较重要的是
- 相对路径的 path 会根据
parentPath转换成绝对路径地址
如上述例子中的 path: "courses" 就转换成 path: "/courses"
- 特殊的 index 属性
对于存在 index 属性且为 true 的路由对象,其会根据父路径地址后面添加一个 / 从而生成一个相对于父路径的决定路径地址。 如上述例子中的 { path: "/courses/", score: 17, routesMeta: Array(3) } 和 { path: "/", score: 6, routesMeta: Array(2) }
- 处理特殊的
?标识符
对于路由配置信息地址中存在? 的存在其将会拆分成 2 个路径匹配地址
For example, /one/:two?/three/:four?/:five? explodes to:
/one/three/one/:two/three/one/three/:four/one/three/:five/one/:two/three/:four/one/:two/three/:five/one/three/:four/:five/one/:two/three/:four/:five
这是一个以深度优先的规则 将路径按照 / 进行截取,然后从后向前依次处理,如果存在?那么当前返回的 result 就会变成[required,""],然后向前收缩的过程中将当前的处理路径与后面的结果进行拼接 从而生成一个 2^N(N 为?个数)的数组
如上述
- 处理
:five?存在?,那么result = [ ":five" , "" ]
- 处理
- 处理
:four?。 存在?。 那么reuslt = [ ":four/:five" , ":four" , ":five" , "" ]
- 处理
- 处理
three。 不存在?,所以不会*2。 那么reuslt = [ "three/:four/:five" , "three/:four" , "three/:five" , "three" ]
- 处理
- 处理
:two?。 存在?。 那么reuslt = [ ":two/three/:four/:five" , ":two/three/:four" , ":two/three/:five" , ":two/three/" , "three/:four/:five" , "three/:four" , "three/:five" , "three" ]
- 处理
- 处理
one。 不存在?,所以不会*2。 那么reuslt = [ "one/:two/three/:four/:five" , "one/:two/three/:four" , "one/:two/three/:five" , "one/:two/three" , "one/three/:four/:five" , "one/three/:four" , "one/three/:five" , "one/three" ]
- 处理
ts
function explodeOptionalSegments(path: string): string[] {
// 1. 将路径按照 / 进行截取分组
// /one/:two?/three/:four?/:five?
// => [ "", "one" , ":two?" , "three" , ":four?" , ":five?" ,]
let segments = path.split("/");
// 如果是一个空字符串 那么直接返回
// ""
if (segments.length === 0) return [];
let [first, ...rest] = segments;
// Optional path segments are denoted by a trailing `?`
let isOptional = first.endsWith("?");
// Compute the corresponding required segment: `foo?` -> `foo`
let required = first.replace(/\?$/, "");
// 处理结尾字符串是否存在 ?
// 如果存在? 那么就会生成返回一个存在两个值的数组 [ ":five" , "" ]
if (rest.length === 0) {
// Intepret empty string as omitting an optional segment
// `["one", "", "three"]` corresponds to omitting `:two` from `/one/:two?/three` -> `/one/three`
return isOptional ? [required, ""] : [required];
}
let restExploded = explodeOptionalSegments(rest.join("/"));
let result: string[] = [];
// All child paths with the prefix. Do this for all children before the
// optional version for all children, so we get consistent ordering where the
// parent optional aspect is preferred as required. Otherwise, we can get
// child sections interspersed where deeper optional segments are higher than
// parent optional segments, where for example, /:two would explode _earlier_
// then /:one. By always including the parent as required _for all children_
// first, we avoid this issue
// 将当前处理的路径节点与已处理好的后面的路径进行拼接,如上述例子的第一步 会将每一个路径加上当前路径前缀
// * 1. 先处理 :five? 存在?,那么result = [ ":five" , "" ]
// * 2.1 处理 :four? 。 存在?。 那么 reuslt = [ ":four/:five" , ":four"]
result.push(
...restExploded.map((subpath) =>
subpath === "" ? required : [required, subpath].join("/")
)
);
// Then, if this is an optional value, add all child versions without
// 如果当前路径中存在 ?
// 那么这一步就是 将后面路径的结果仍然赋值一份保存到后面
// * 2.2 处理 :four? 。 存在?。 那么 reuslt = [ ":four/:five" , ":four" , ":five" , "" ]
if (isOptional) {
result.push(...restExploded);
}
// for absolute paths, ensure `/` instead of empty segment
// 这一步主要处理特殊的 ""
return result.map((exploded) =>
path.startsWith("/") && exploded === "" ? "/" : exploded
);
}3. 权重计算
对于路由的权重计算主要为了以下几点目标
- 让路径更长的路由地址排列在数组的前面,这样对于
/courses/:id就会优先于/courses - 相同路径长度的地址
- 对于存在
index其优先级会小于正常的路径地址 - 也会优先于
:xx的路径
- 对于存在
计算规则如下
将路径按照 / 进行分割, 然后每一个长度加 1 分 ,
如果存在 * 那么就 -2
如果存在 index 那么就 加 2 分
然后按照数组中的每一个值进行加分,即 "" 的1分 , courses的10分 , :id的3分
例如
/courses/one/:id/info 权重分数: /分割数组长度为 5 分 + "" 的 1 分 + courses 的 10 分 + one 的 10 分 + :id 的 3 分 + info 的 10 分 = 5+1+10+10+3+10 = 39 分
/courses/ 这个index为true 权重分数: /分割数组长度为 3 分 + "" 的 1 分 + courses 的 10 分 + "" 的 1 分 + index 的 2 分 = 3+1+10+1+2 = 17 分
/courses/one2/three/* 权重分数: /分割数组长度为 5 分 + "" 的 1 分 + courses 的 10 分 + one 的 10 分 + three 的 10 分 + *的负 2 分 = 5+1+10+10+10-2 = 34 分
注意
我们发现对于 index:true 和 /:xxx的权重分数都是 3 分,所以在 V6 中其两个是相等的
ts
/**
* 计算路径的权重
*
*
*
* /courses/one/:id/info
* 权重分数: /分割数组长度为 5分 + "" 的1分 + courses的10分 + one的10分 + :id的3分 + info的10分 = 5+1+10+10+3+10 = 39分
* /courses/ 这个index为true
* 权重分数: /分割数组长度为 3分 + "" 的1分 + courses的10分 + "" 的1分 + index的2分 = 3+1+10+1+2 = 17分
* /courses/one2/three/*
* 权重分数: /分割数组长度为 5分 + "" 的1分 + courses的10分 + one的10分 + three的10分 + *的负2分 = 5+1+10+10+10-2 = 34分
* @param path
* @param index 是否设置了 index 属性
* @returns
*/
function computeScore(path: string, index: boolean | undefined): number {
// 将路径按照 / 进行分割
let segments = path.split("/");
// 初始权重 为分割数组的长度
let initialScore = segments.length;
// 如果存在 * 那么就 -2
if (segments.some(isSplat)) {
initialScore += splatPenalty;
}
// 如果存在 index 那么就 加2分
if (index) {
initialScore += indexRouteValue;
}
return segments
.filter((s) => !isSplat(s))
.reduce(
(score, segment) =>
score +
// 如果是以 : 开头的 那么权重分数为 3
(paramRe.test(segment)
? dynamicSegmentValue
: // 如果是 “” 那么权重分数为 1
segment === ""
? emptySegmentValue
: // 默认权重分数为10
staticSegmentValue),
initialScore
);
}4. 权重排序
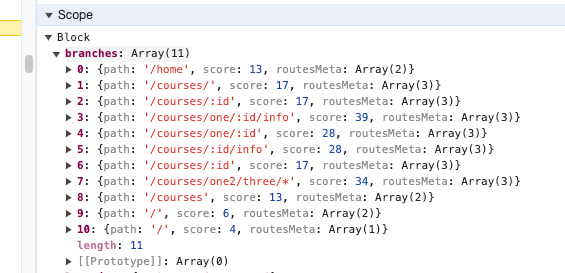
对于所有的路由进行权重排序
- 先按照 score 是否相同,如果不同 score 高的放在前面
- 如果 score 不相同 那么通过 compareIndexes() 进行排序 compareIndexes 是按照路由在树中每一个层级的顺序下标,如果全部相同那就不动,如果有一个不同就判断最后一层的下标大小,下标大的放在后面
目的
- 路径长的其权重高,所以会将所有的长路径路由排在前面
 =>
=> 
- 对于权重相同的,如相同定义方式在同一父路由下的路由,那么就按照 childIndex(下标)进行排序,这样就不会将后面定义的路由优先级大于前面的
源码
- 先按照 score 排序
ts
function rankRouteBranches(branches: RouteBranch[]): void {
branches.sort((a, b) =>
// 1. 先按照score 是否相同
a.score !== b.score
? // 如果不同score高的放在前面
b.score - a.score // Higher score first
: // 如果score 不相同 那么通过 compareIndexes() 进行排序
compareIndexes(
a.routesMeta.map((meta) => meta.childrenIndex),
b.routesMeta.map((meta) => meta.childrenIndex)
)
);
}- 相同 score 的情况下对于相同父路由下的两个路由按照下标进行排序
ts
/**
* 主要用于判断相同父路由下的两个路由按照下标进行排序
* 下标的小的排在前面
* @returns
*/
function compareIndexes(a: number[], b: number[]): number {
// 判断路由的父级层级中每一层中的下标是否都相同
// const a = [0,3,10,1] ; const b = [0,3,10,10]
// siblings === true
// 这个代表当前两个路由是在相同的父路由下
let siblings =
a.length === b.length && a.slice(0, -1).every((n, i) => n === b[i]);
//
return siblings
? // If two routes are siblings, we should try to match the earlier sibling
// first. This allows people to have fine-grained control over the matching
// behavior by simply putting routes with identical paths in the order they
// want them tried.
// 如果在相同的父路由下 那就按照下标下的在前面
a[a.length - 1] - b[b.length - 1]
: // Otherwise, it doesn't really make sense to rank non-siblings by index,
// so they sort equally.
// 否则视为相同
0;
}5. 路由匹配 (matchRouteBranch)
通过之前的 路径扁平化处理及绝对路径、index类型的 , /:xxx?类型的处理 ;2. 权重计算及排序 从而将我们的路由数据按照路径越长(大概率)排在前面,并将路由的真实路径按照配置的上下级关系按照顺序存放在 routeMeta 属性中(其中的每级路径也转换成相对路径);
如 /courses/one/:id/info 其 routesMetas 属性就是
json
[
{
"caseSensitive": false, // 是否大小写忽略
"childrenIndex": 0, // 路由的层级
"relativePath": "/" // 此层级中对应的 路由
},
{
"caseSensitive": false,
"childrenIndex": 1,
"relativePath": "courses"
},
{
"caseSensitive": false,
"childrenIndex": 2,
"relativePath": "/one/:id/info"
}
]那么在这一步,我们就将一个真实的 url 路径地址 pathname,通过从前向后分段匹配上述的 "relativePath",从而知道当前路由信息是否匹配当前 url 地址。
在此过程中其主要通过以下几个步骤
- 通过
compilePath()将relativePath转换成对应的 正则表达式,并提取中其中/*,/:id等对应的 params 对象 - 通过
pathname.match(matcher)匹配,从而判断 url 地址是否匹配,并获取中其中对应的特殊变量值['/one/12/three/345/five', '12', '345'] - 通过遍历
compilePath()中 params ,然后根据index从而将 每一个 params 的 key 与其对应的值对应
下面我们分别具体讲解其步骤
1. compilePath()转换正则表达式过程
将路由配置信息的 path 转换成对应的 正则表达式主要是安装以下情况
通过这一步骤为了以下目的
- 对于
:xxx可以生成通用的正则匹配,并提取出对应的key - 对于 特殊的
*的处理,主要为以下几种特殊情况/*、/、xxx*、/*xxxxxx
具体流程如下
处理特殊的
:xxx和:xxx?规则,将其转换成/?([^\\/]+)?表达式 ,和[{ paramName : "xxx" }]处理:two:two?主要是将其转换成 可选正则表达式/?([^\\/]+)?或者 不可选/?([^\\/]+)?/one/:two/three/:fout?=>/one/([^\\/]+)/three/?([^\\/]+)/:two=>/([^\\/]+)不可选表达式{ paramName : "two" , isOptional: false }/:fout?=>/?([^\\/]+)?不可选表达式{ paramName : "four" , isOptional: true }处理以
/*/,xxx*结尾的 对于存在\*为结尾的分为两种情况/_直接这种的regexp += "(._)$"xxxx*直接这种的regexp += "(?:\\/(.+)|\\/*)$"同时 params 添加一个{ paramName: "_" }将匹配的值存储在 key 为_的键上
处理以
/*开头的 直接将其转换成/最后在后面加上特地的表达式 从而忽略下级路径 对于是最后一段的路径 那么就在正则的末尾加上
\\/\*$
源码
ts
function compilePath(
path: string,
caseSensitive = false,
end = true
): [RegExp, CompiledPathParam[]] {
warning(
path === "*" || !path.endsWith("*") || path.endsWith("/*"),
`Route path "${path}" will be treated as if it were ` +
`"${path.replace(/\*$/, "/*")}" because the \`*\` character must ` +
`always follow a \`/\` in the pattern. To get rid of this warning, ` +
`please change the route path to "${path.replace(/\*$/, "/*")}".`
);
let params: CompiledPathParam[] = [];
let regexpSource =
"^" +
path
// 忽略结尾的 `/*` , `/` 还包含特殊的 `///*` , `///`
// 主要是将结尾的 `/*` , `/` 类型的截取掉,因为 /one/* 其实就代表 /one xxxxx
// /one/* => /one /one/ => /one /one/** => /one/*
.replace(/\/*\*?$/, "") // Ignore trailing / and /*, we'll handle it below
// 将 `/*` 开始的直接转换成 `/` 因为后面的已经没有意义了
// /*one/xxx => /
.replace(/^\/*/, "/") // Make sure it has a leading /
// 处理特殊的字符
// 将其转换成 * => \\*
// "12*1231" => '12\\*1231'
.replace(/[\\.*+^${}|()[\]]/g, "\\$&") // Escape special regex chars
// 处理 `:two` `:two?`
// 主要是将其转换成 可选正则表达式 /?([^\\/]+)? 或者 不可选 "/?([^\\/]+)?"
// /one/:two/three/:fout? => /one/([^\\/]+)/three/?([^\\/]+)
// /:two => /([^\\/]+) 不可选表达式 { paramName : "two" , isOptional: false }
// /:fout? => /?([^\\/]+)? 不可选表达式 { paramName : "four" , isOptional: true }
.replace(
/\/:([\w-]+)(\?)?/g,
(_: string, paramName: string, isOptional) => {
params.push({ paramName, isOptional: isOptional != null });
return isOptional ? "/?([^\\/]+)?" : "/([^\\/]+)";
}
);
// 1. 处理末尾的 /one/two*
// 将其转换成 /one/two(?:\\/(.+)|\\/*)$
// 2. 处理特殊的 `*` || `/*` => (.*)$
if (path.endsWith("*")) {
params.push({ paramName: "*" });
regexpSource +=
path === "*" || path === "/*"
? "(.*)$" // Already matched the initial /, just match the rest
: "(?:\\/(.+)|\\/*)$"; // Don't include the / in params["*"]
} else if (end) {
// When matching to the end, ignore trailing slashes
// 结尾加上 `\\/*$` 从而匹配所有的下级
regexpSource += "\\/*$";
} else if (path !== "" && path !== "/") {
// If our path is non-empty and contains anything beyond an initial slash,
// then we have _some_ form of path in our regex, so we should expect to
// match only if we find the end of this path segment. Look for an optional
// non-captured trailing slash (to match a portion of the URL) or the end
// of the path (if we've matched to the end). We used to do this with a
// word boundary but that gives false positives on routes like
// /user-preferences since `-` counts as a word boundary.
regexpSource += "(?:(?=\\/|$))";
} else {
// Nothing to match for "" or "/"
}
// 生成对应的 正则表达式
let matcher = new RegExp(regexpSource, caseSensitive ? undefined : "i");
return [matcher, params];
}2. 通过正则表达式的分段值,然后与获取的 params 数组一一对应从而生成当前 url 中特殊的 可变地址变量
ts
// '/one/12/three/345/five'.match(new RegExp('/one/([^\\/]+)/three/?([^\\/]+)?/five/'))
// 结果为: ['/one/12/three/345/five', '12', '345']
// 匹配的 pathname
let matchedPathname = match[0];
//
let pathnameBase = matchedPathname.replace(/(.)\/+$/, "$1");
// 获取match匹配后 获取的占位符的值 如上述的 ['12', '345']
let captureGroups = match.slice(1);
// 将匹配的结果赋值给对应的 paramName
// memo = { "two" : "12" , four : "345" }
let params: Params = compiledParams.reduce<Mutable<Params>>(
(memo, { paramName, isOptional }, index) => {
// We need to compute the pathnameBase here using the raw splat value
// instead of using params["*"] later because it will be decoded then
if (paramName === "*") {
let splatValue = captureGroups[index] || "";
pathnameBase = matchedPathname
.slice(0, matchedPathname.length - splatValue.length)
.replace(/(.)\/+$/, "$1");
}
// 按照顺序获取对应的值
const value = captureGroups[index];
// 如果存在变量,但是值为空,那么就赋值默认值undefined
if (isOptional && !value) {
memo[paramName] = undefined;
} else {
// 修改对应key的值
memo[paramName] = safelyDecodeURIComponent(value || "", paramName);
}
return memo;
},
{}
);渲染路由
对于非 DATARouter 类型的路由,其渲染路由的过程非常简单,其核心就是 _renderMatches()的过程,这是一个 从右向左的过程
ts
/**
* 渲染路由
* @param matches
* @param parentMatches
* @param dataRouterState
* @param future
* @returns
*/
export function _renderMatches(
matches: RouteMatch[] | null,
parentMatches: RouteMatch[] = [],
// 服务端渲染
dataRouterState: RemixRouter["state"] | null = null,
future: RemixRouter["future"] | null = null
): React.ReactElement | null {
if (matches == null) {
return null;
}
let renderedMatches = matches;
// reduceRight `从右向左` 递归处理
// TODO: 为什么从右向左
return renderedMatches.reduceRight((outlet, match, index) => {
let matches = parentMatches.concat(renderedMatches.slice(0, index + 1));
// 获取当前 match 对应的组件
// 设计到
let getChildren = () => {
let children: React.ReactNode;
if (match.route.Component) {
// Note: This is a de-optimized path since React won't re-use the
// ReactElement since it's identity changes with each new
// React.createElement call. We keep this so folks can use
// `<Route Component={...}>` in `<Routes>` but generally `Component`
// usage is only advised in `RouterProvider` when we can convert it to
// `element` ahead of time.
children = <match.route.Component />;
} else if (match.route.element) {
children = match.route.element;
} else {
children = outlet;
}
return (
<RenderedRoute
match={match}
routeContext={{
// 当前子路由对应的 组件实例对象
outlet,
// 当前匹配的 matches
matches,
isDataRoute: dataRouterState != null,
}}
children={children}
/>
);
};
return getChildren();
}, null as React.ReactElement | null);
}
/**
* 渲染Route的Component 或者 element 属性内容
* 核心主要是借助于 RouteContext.Provider 将 { outlet matches }传递给当前组件下的 outlet
* @param param0
* @returns
*/
function RenderedRoute({ routeContext, match, children }: RenderedRouteProps) {
let dataRouterContext = React.useContext(DataRouterContext);
// Track how deep we got in our render pass to emulate SSR componentDidCatch
// in a DataStaticRouter
if (
dataRouterContext &&
dataRouterContext.static &&
dataRouterContext.staticContext &&
(match.route.errorElement || match.route.ErrorBoundary)
) {
dataRouterContext.staticContext._deepestRenderedBoundaryId = match.route.id;
}
return (
<RouteContext.Provider value={routeContext}>
{children}
</RouteContext.Provider>
);
}